Computers may look very different, but the components installed are standard. The major difference among most machines is the brand of hardware installed. The hardware components—video card, processor, memory, motherboard and hard drive—are the same for all computer systems.
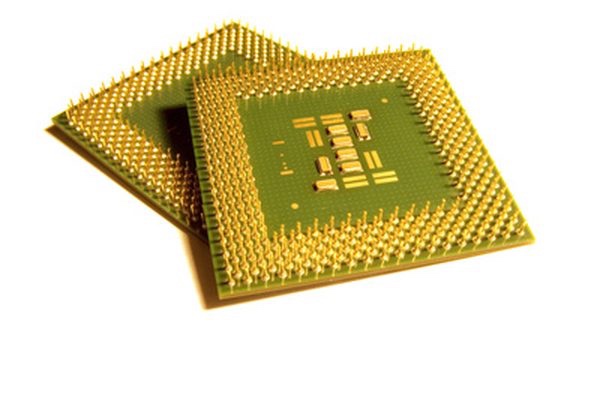
The CPU is the “brains” of the computer. The central processing unit provides the calculations and manipulation of data sent from the user. Each time the user clicks a key, executes an application or browses the Web, the CPU reads the code involved and returns the response to the user. The CPU works closely with memory, which is the component that sends stored data to the unit.
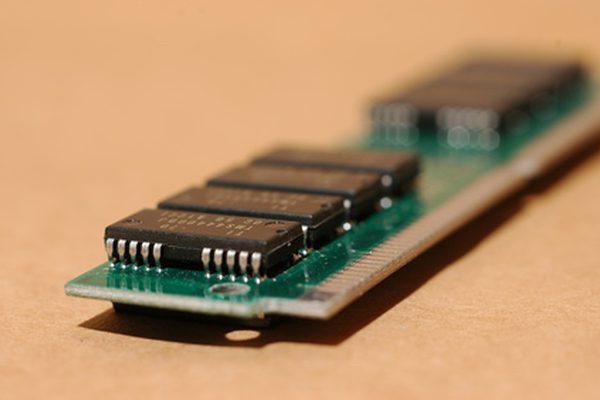
RAM is variable in a computer. Older computers had only a few dozen megabytes of RAM installed. When personal computers became popular in the 1990s, computers had 32 megabytes of memory. Motherboards and software now require at least one gigabyte to function. RAM contains the information during the time the computer is on. After the machine is turned off, the information in RAM is lost.
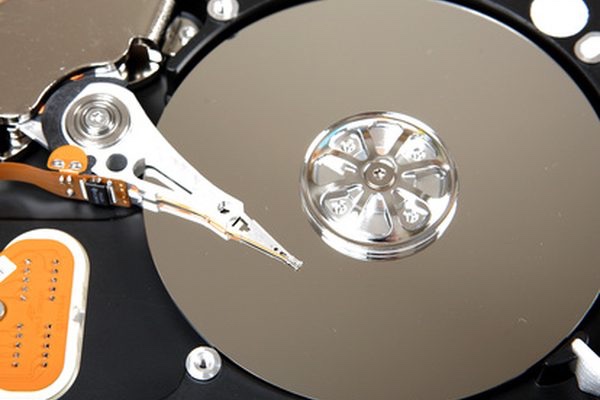

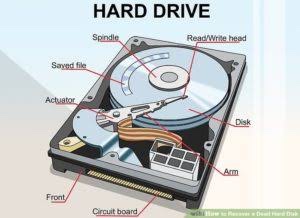
Unlike RAM, the hard drive stores data even after the machine is turned off. A hard drive is the storage unit for the machine. Saved documents and applications are stored on the hard drive using magnetism. The hard drive is made up of small platters with a moving head. The platters spin as the head moves back and forth to retrieve and store data.
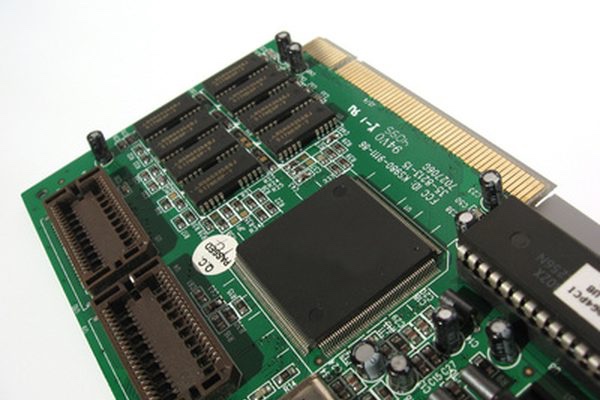

The video card provides the image seen on the monitor. The video card is attached to a monitor using a VGA cable. Some video cards have two monitor connections. This allows the user to attach two monitors to the computer, so the desktop can be spread across both monitors for better usability.
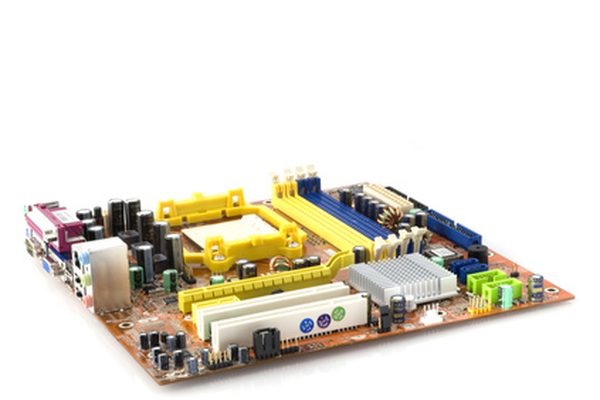

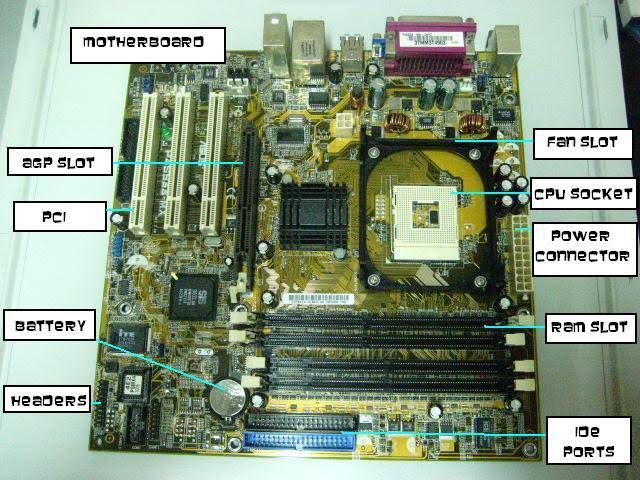
Each component is attached to the motherboard. The motherboard receives power from the computer’s power supply. The motherboard allows all the components to communicate, including the CPU. The motherboard also contains controllers, which are circuits that help the operating system work with hardware such as the hard drive.
The two typical components of a CPU include the following:
The arithmetic logic unit (ALU), which performs arithmetic and logical operations.
The control unit (CU), which extracts instructions from memory and decodes and executes them, calling on the ALU when necessary.PART’S OF CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT
PART’S OF RANDOM ACCESS MEMORY

PART’S OF HARD DRIVE
PART’S OF VIDEO CARD

Watch the video below to learn about the buttons, ports, and slots on a desktop computer.
Computer case
The basic parts of a desktop computer are the computer case, monitor, keyboard, mouse, and power cord. Each part plays an important rolewhenever you use a computer.
The computer case is the metal and plastic box that contains the main components of the computer, including the motherboard, central processing unit (CPU), and power supply. The front of the case usually has an On/Off button and one or more optical drives.
Computer cases come in different shapes and sizes. A desktop case lies flat on a desk, and the monitor usually sits on top of it. A tower case is tall and sits next to the monitor or on the floor. All-in-one computers come with the internal components built into the monitor, which eliminates the need for a separate case.
Monitor

Newer monitors usually have LCD(liquid crystal display) or LED (light-emitting diode) displays. These can be made very thin, and they are often called flat-panel displays. Older monitors use CRT (cathode ray tube) displays. CRT monitors are much larger and heavier, and they take up more desk space.
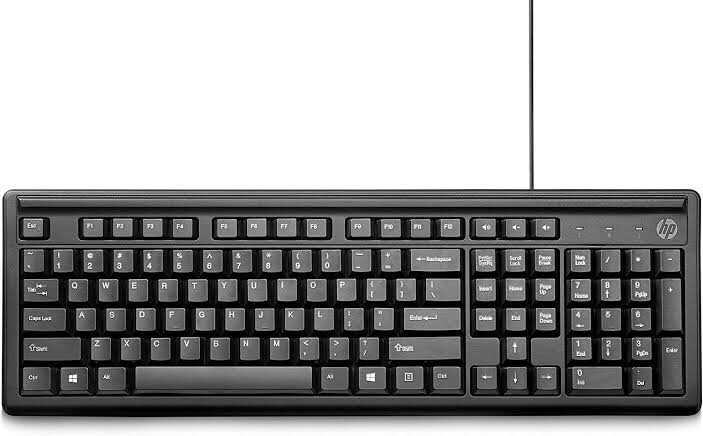
Keyboard
The keyboard is one of the main ways to communicate with a computer. There are many different types of keyboards, but most are very similarand allow you to accomplish the same basic tasks.

Mouse

The mouse is another important tool for communicating with computers. Commonly known as a pointing device, it lets you point to objects on the screen, click on them, and movethem.
There are two main mouse types: optical and mechanical. The opticalmouse uses an electronic eye to detect movement and is easier to clean. The mechanical mouse uses a rolling ball to detect movement and requires regular cleaning to work properly.
Mouse alternatives
There are other devices that can do the same thing as a mouse. Many people find them easier to use, and they also require less desk space than a traditional mouse. The most common mouse alternatives are below.
- Trackball: A trackball has a ball that can rotate freely. Instead of moving the device like a mouse, you can roll the ball with your thumb to move the pointer.

Touchpad: A touchpad—also called a trackpad—is a touch-sensitive pad that lets you control the pointer by making a drawing motion with your finger. Touchpads are common on laptop computers.

Introduction
Take a look at the front and back of your computer case and count the number of buttons, ports, and slotsyou see. Now look at your monitor and count any you find there. You probably counted at least 10, and maybe a lot more.
Each computer is different, so the buttons, ports, and sockets will vary from computer to computer. However, there are certain ones you can expect to find on most desktop computers. Learning how these ports are used will help whenever you need to connect something to your computer, like a new printer, keyboard, or mouse.
Peripherals you can use with your computer
The most basic computer setup usually includes the computer case, monitor, keyboard, and mouse, but you can plug many different types of devices into the extra ports on your computer. These devices are called peripherals. Let’s take a look at some of the most common ones.
- Printers: A printer is used to print documents, photos, and anything else that appears on your screen. There are many types of printers, including inkjet, laser, and photo printers. There are even all-in-one printers, which can also scan and copy documents.

- Scanners: A scanner allows you to copy a physical image or document and save it to your computer as a digital (computer-readable) image. Many scanners are included as part of an all-in-one printer, although you can also buy a separate flatbed or handheld scanner.
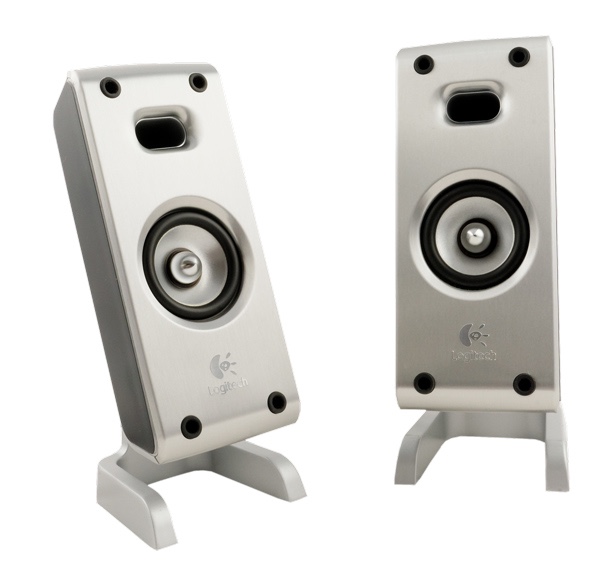
- Speakers/headphones:Speakers and headphonesare output devices, which means they send information from the computer to the user—in this case, they allow you to hear sound and music. Depending on the model, they may connect to the audio port or the USB port. Some monitors also have built-in speakers.

- Microphones: A microphone is a type of input device, or a device that receives information from a user. You can connect a microphone to record sound or talk with someone else over the Internet. Many laptop computers come with built-in microphones.
- Web cameras: A web camera—or webcam—is a type of input device that can record videos and takepictures. It can also transmit video over the Internet in real time, which allows for video chat or video conferencing with someone else. Many webcams also include a microphone for this reason.

Digital cameras: A digital camera lets you capture pictures and videos in a digital format. By connecting the camera to your computer’s USB port, you can transfer the images from the camera to the computer.
Mobile phones, MP3 players, tablet computers, and other devices:Whenever you buy an electronic device, such as a mobile phone or MP3 player, check to see if it comes with a USB cable. If it does, this means you can most likely connect it to your computer.
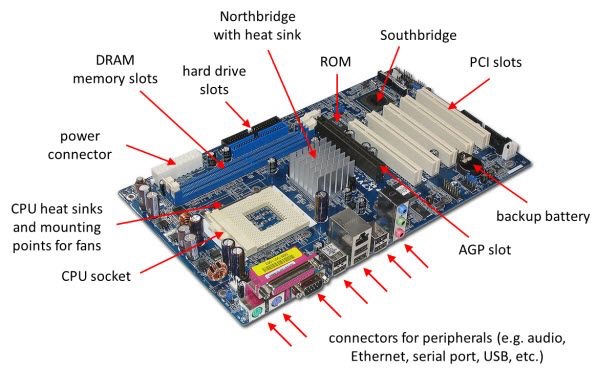
Memory Sockets
A typical motherboard has at least two sockets for Random Access Memory (RAM). RAM acts as a high-speed system for temporarily storing the data needed by programs while they are running. When the processor needs instructions, it receives them from the RAM, and when you save a document or file, it goes from the RAM to the hard drive.
Hard Drive Connectors
Generally, a motherboard has at least two hard drive connectors. Current motherboards use Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA) hard drive connectors, which have L-shaped curves to ensure that cables are connected in the correct direction. The older Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE) connector uses two rows of 20 pins each. Some motherboards have connectors for both SATA and IDE drives. The computer’s CD or DVD drive also connects to an IDE or SATA interface.
Floppy Drive Connector
Although few modern computers use floppy drives for storage, many motherboards continue to include floppy drive connectors to support legacy devices. A floppy drive connector has two rows of 17 pins each.
Peripheral Connectors
Motherboards have connectors for different types of peripherals, usually located on a back plane that remains exposed on the back of the computer case when the tower is closed. The most common peripheral connection is the Universal Serial Bus (USB) connection, while some motherboards also have connections for audio speakers along with ports for FireWire, serial and parallel devices. Some motherboards have additional “headers,” or banks of pins, that can be used to connect additional peripheral ports on the front of the computer case.
Add-on Card Connectors
Many motherboards have connectors for computer add-on cards. These connectors are long slots into which the cards are inserted. There are several types of add-on card connectors. Some of the most common include Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe) and Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP), used mainly for video cards, and conventional Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI), used for other types of add-on cards such as sound cards and storage controllers.
Power Connector
Every motherboard has at least one power connector. This connector is used to bring power from the computer’s main power supply to all of the computer’s components. Because some of today’s desktop computers have very high power requirements, some motherboards have additional ports for auxiliary power connectors.
Case Connectors
On the side of the motherboard closest to the front of the computer case are the case connectors, a bank of pins to which very small wires attach. The case connectors are used for the power and status lights on the front of the computer case, as well as the power button that turns the computer on.
Most vital parts of computer

COMPUTER HARDWARE


